PGOPHER can do a traditional force
field analysis, calculating vibrational frequencies, the
l
matrix, isotope shifts, rotational constants, centrifugal
distortion constants and Coriolis coupling constants from force
constants and geometry. The force constants and geometry can be
derived by fitting to any combination of the calculated
quantities. The calculations are similar to those done by the
ASYM20/ASYM40 program of Hedberg and Mills (1993, 2000), though
implemented in a more flexible way, and these papers give a good
outline of the methodology and how the calculations are
performed. The VIBCA program (
http://www.ifpan.edu.pl/~kisiel/vibr/vibr.htm)
also performs similar calculations.
The force field can be expressed in terms of valence or
symmetry coordinates. A typical analysis will include several
isotopologues and might have a data file structured something
like this:
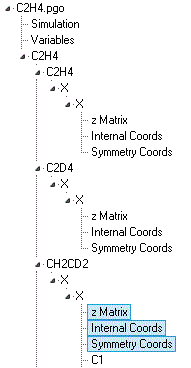
Note the various single and multiple objects:
- A single Global Variables object
which contains geometric variables and force constants common
to all isotopologues.
- A z Matrix for each
isotopologue, which specifies the geometry. The use of
variables means this will be identical for all
isotopologues, except for the masses.
- An (optional) Internal
Coordinates object for each isotopologue, which
specifies the valence coordinates and force constants. The use
of variables means this will be identical for all
isotopologues.
- An (optional) Symmetry
Coordinates object for each isotopologue, which
specifies the combinations of valence coordinates to use. The
use of variables means this will only differ for
isotopologues of different symmetry.
A Cartesian Coordinates
object may also be present; the exact combination of objects
used depends on the required calculation. Nuclear Co-ordinates and Vibrational Modes objects will
also be present, automatically created and updated from the
force field analysis objects listed above.
The current version of the program does not explicitly make
use of symmetry for the force field analysis, but it is implicit
in the way the force constants and geometry are specified. The
current version of PGOPHER is restricted to harmonic terms, but
the program is structured so that anhamonic terms can be added
in future. The units are currently less flexible than for
rotational calculations; the overall mixture units must be set
to cm-1, the geometry specified in Angstroms
and degrees and force constants (for stretches) in millidyne/Å
= aJ/Å2 (1 millidyne/Å = 1 aJ/Å2
= 100 J/m2 = 100 N/m). For a full discussion of the
units see Hedberg and Mills (1993).
