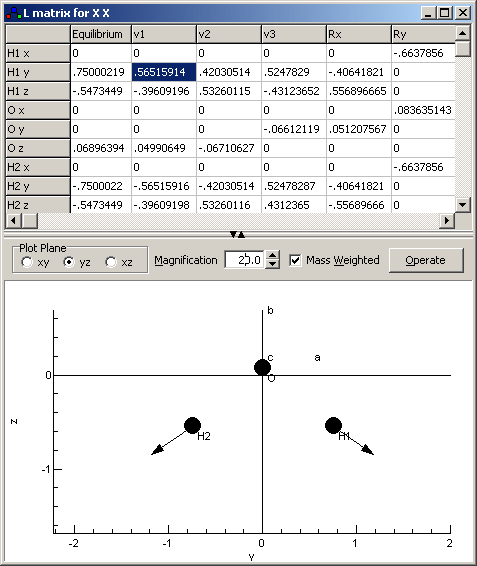
The
lower
panel shows the atom positions, and a normal mode motion if
a mode is selected. a,
b, and c are the principal
inertial axes, which are calculated from the given atomic
positions.
|
 |
Drag to resize the upper and lower parts.
|
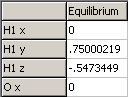 |
Equilibrium positions of the atoms, in Å. These
should be with respect to the centre of mass; if not see
under the Operate button. |
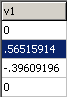 |
l matrix in
Cartesian co-ordinates in one of two possible forms:
- If "Mass
Weighted" is checked the values correspond to
relative atomic displacements, and the units are
1/sqrt(atomic mass units).
- If "Mass
Weighted" is checked the values are
dimensionless. In this form the matrix should be
orthogonal; see under the Operate
button for options to check and correct this.
The conversion factor between the two for any given value is
Sqrt(mass of Nucleus).
|
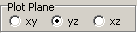 |
Select plane to plot
|
  |
This controls the length of the arrows plotted on each
atom to show the motion of the atom in the selected normal
mode. The number is the multiple of the zero point motion,
assuming the motion is harmonic. If you can't see any
arrows, you may need to increase the value set here.
|
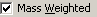 |
Check to show l
matrix elements divided by sqrt(mass); uncheck to show as
dimensionless numbers. The numbers can be edited in either
mode.
|
 |
Show Translational and Rotational normal mode
transformations. |
 |
This brings up a menu with the following options:
|